Do you know that there is a condition where children aren’t able to move their tongue freely, chew or speak as they grow. Also that this is nothing to do with developmental or growth changes and is restricted to a an oral problem?
Teeth and their well-being is what many of strive to give our kids from a very young age. While we follow general oral hygiene and practice the necessary steps that are required for general oral care, not all of us are aware of the many congenital and developmental problems that affect the mouth, and in turn the growth and care of teeth.
WHAT IS TONGUE TIE?
Tongue Tie is one such congenital oral condition that is often overlooked or misunderstood. Also called ‘Ankyloglossia’ or ‘anchored tongue’, it is observed very often by parents at a very late stage, once the child has started talking or eating and this condition is hampering normal oral functions.
Ranging from a mild form to a severe state, tongue tie is seen at birth and causes many different difficulties that affect kids in myriad different ways. This condition is caused by the structural abnormality of the lingual frenum. The frenum is the cord that extends from under the tongue to the mouth floor. When this lingua frenum is short or restricts tongue movements, this is the condition that results.

Normally the frenum is elastic and does not interfere with eating, sucking, clearing food duing swallowing or speech. But if it is short, thick or broad, it can attach the tongue to the mouth floor causing problems with speech, eating and even tooth growth.
While mild tongue tie sometimes goes unnoticed and does not affect the day to day life of the child, severe tongue tie can cause lifelong debilitating effects.
What are the side-effects of Untreated tongue tie?
Untreated tongue tie can have wide ranging effects, affecting the structure and appearance of face and teeth, and also interfering with oral function. Breastfeeding, eating, swallowing, digestion, teeth and speech can be affected when they are little, and kissing and social skills are affected further into adulthood.
Infants and Babies face the below challenges that include;
- Impact on the milk supply
- Stoppage of breastfeeding
- Loss of weight
- Sleep deprivation
- Chewing and swallowing especially intake of solids being affected
As babies grow, the problems only persist and gradually increase
- Inability to chew age-appropriate foods
- Gagging, vomiting of foods
- Dribbling of saliva and delayed speech development
- Loss of self-confidence
ORAL HYGIENE AND DENTAL HEALTH
Besides these obvious problems, the main impact of tongue tie is in the growth and development of teeth in children. If the frenulum is attached very high on the gum line, it can pull down the gums from the central incisors. The tongue tie can also cause the tongue to become misshapen which can cause teeth to grow haphazardly or at an angle. 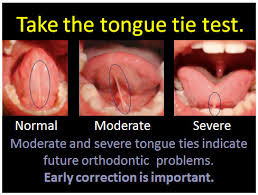
The reduced tongue mobility and habitual wrong tongue posture that results from tongue tie is accompanied by messy eating habits, resulting in food debris remaining in the mouth and teeth, and causing caries. Salivary profusion caused due to the inability to swallow manifests itself in different ways. Younger child dribble profusely, while older kids adapt, either by slurping frequently, keeping the mouth small during speech, or reducing speech altogether. They also face an involuntary and embarrassing dribble of saliva.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENTS FOR TONGUE-TIE ?

Tongue tie is a barely recognized but serious problem, because of the way it generally goes unnoticed, yet can cause potentially serious and life long damage to teeth and the oral cavity. It can be manifested in a variety of ways, and a pediatrician or pediatric dentist will be able to identify this cause if they notice any significant increased salivation, dribbling of saliva, mouth odour or damage/caries to teeth.
Parents who find the child having difficulties, should then go in for treatment if there has been any malocclusions caused by tongue pressure on the front or side teeth. Since the tongue has a limited range of movements, there are many resultant effects which include:
- Poor swallowing and a resultant risk of anterior open bite
- Mouth breathing and allergies/issues due to this
- Permanently open mouthed posture due to continued imbalance in skeletal structure
- Restriction in the development of the dental arch and facial bones
Minor surgery is required to correct this condition when diagnosed at an earlier stage. If there are significant and serious oral and articulating issues, the child will need additional speech therapy and preventive measures for treating caries and other teeth issues.